On its own, opting for a pricing method to follow your business strategy is equally difficult and important task. After all, it’s part art, part science. Deciding on the amount you want to charge your customers for your products is a huge step to setting your pricing strategy in the long run. There is no sure-fire way to determine the best pricing strategy for each business but there are some pricing methods and guidelines, which we hope to present with this post, that will ultimately help you make an informed decision because we’re like that, we like to help. Here we go.
Pricing methods can be divided into two major groups:
- Cost-oriented methods
- Market-oriented methods
Each group consists of several pricing methods which we’ll present further down.
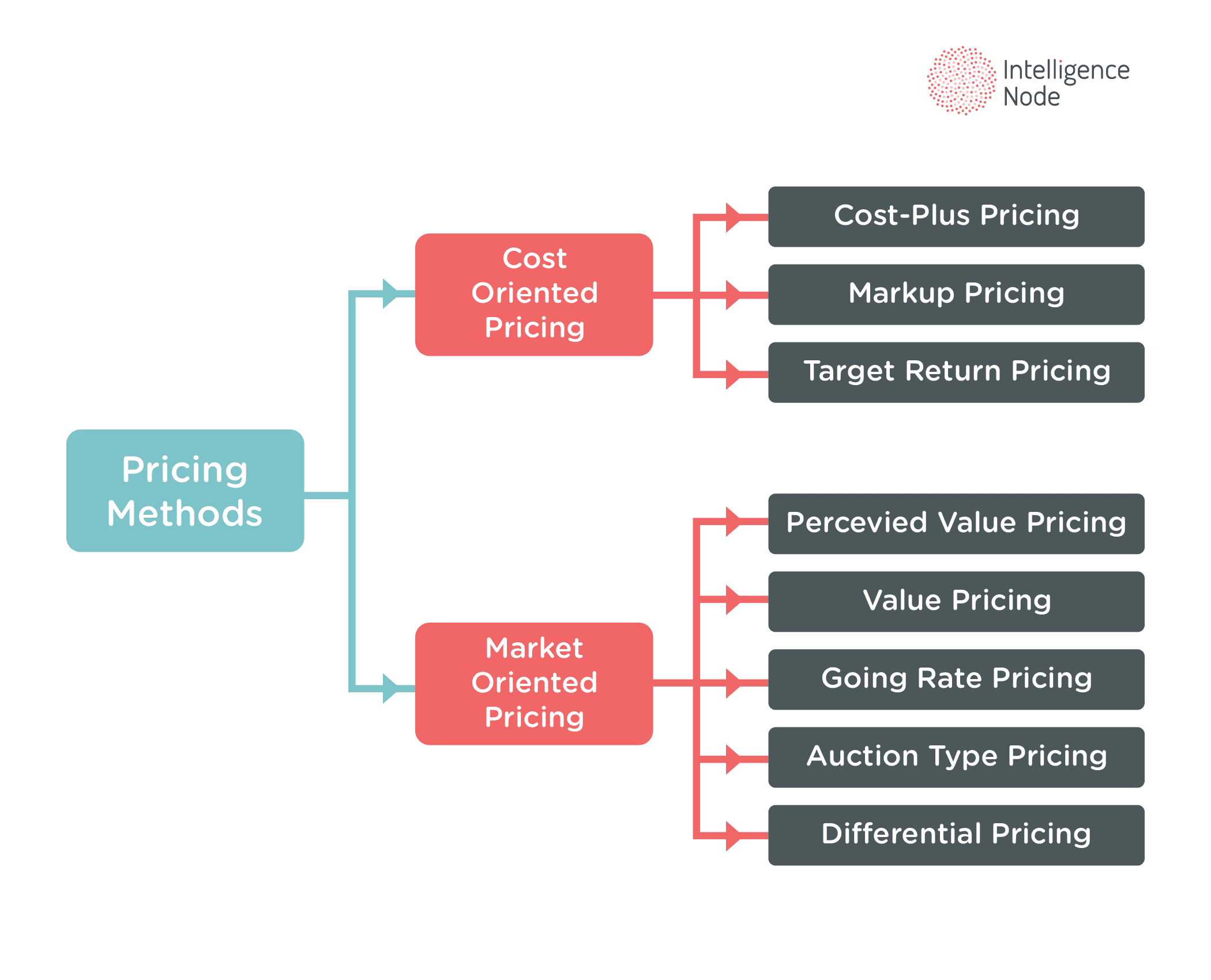
Classification of pricing methods
Cost-oriented pricing methods
This is where the cost acts as a basis for determining the price of the final product. The main advantage of these methods is that the prices cover all the costs and directly add to profit. On the other hand, the don’t take into consideration market factors like competition, demand and consumers’ perceived value.
Cost-oriented pricing methods include the following ways of pricing:
1. Cost-plus pricing
In what is probably the simplest pricing method, a company adds a markup percentage to the overall production costs and thus forms the price. The markup is the profit percentage calculated on total cost. For instance, if the cost of the product is $10 and the company expects a 10 percent profit, then the selling price will be $11.
2. Markup pricing
Similar to cost-plus pricing method, the markup is calculated as a percentage of the selling price and not the cost price. If the cost of the product is $10 and the company wants to earn the markup of 20 percent on sales, the price is calculated with the following equation:
Price = product cost / 1 – markup
which in our case is:
Price = 10 / 1 – 0.20 = 12.5
Hence, the company will set the price at $12.5 and earn a profit of $2.5 per product.
3. Target-return pricing
This pricing method focuses on the required ROI rate from the sales of goods. Let’s say that a business invested a $100,000 and expects a 20 percent ROI ($20,000). The target-return price is calculated like this:
Target-return price = product cost + (desired return x capital invested) / unit sales
Based on the previous example and calculating 10000 unit sales, that would translate to:
Target-return price = 10 + (0.20 x 100000) / 10000 = 12

Graphical representation of target-return pricing formula (Image Source)
This concludes the overview of cost-oriented pricing methods. Let’s move on to the second group.
Market-oriented pricing methods
As the name cunningly suggests, the price using these methods is calculated on different market conditions. Market-oriented pricing presents a more accurate and effective market price representation and “speaks” directly to customers. However, it requires a much-desired market research in order to establish the market factors as guides to successful pricing.
1. Perceived value pricing
In this pricing method, a business, more than anything, sets the price based on the customer’s perception of its offering. This pricing method accounts all the other elements of marketing mix (product, place, promotion) to influence the customers. As an example, a customer buys a more expensive product such as Apple’s iPhone despite having lower-priced smartphones available in the market. The reason for such decision lies in Apple alignment with perceived value pricing where the customer has no problem paying extra for better quality and durability or perhaps for the status symbol.
2. Value pricing
The basic principle here is providing low priced products with high-quality levels. Even though the price is low, it is set accordingly to minimize the cost of production while preserving quality at the same time. A good example would be Tata Motors, whose Tata Nano was designed with only the necessary features at a low price while retaining quality.
3. Going-rate pricing
This pricing method is pretty simple (yay!) – a business takes into account the prices of its direct competition and uses them as a basis for its own prices. Going-rate pricing can be divided into three subgroups:
- Parity pricing – the price is the same price as that of the biggest competitor;
- Premium pricing – the price is a little higher, usually accounting the fact the product has additional features unlike competitor’s product;
- Discount pricing – the price is a little lower if the product lacks features that competitor’s product has.
This pricing method is one of the more popular with homogeneous goods like steel, paper, fertilizer, etc. (products with less variations in features) as it provides a good chance for a business to get a fair return on their prices by charging the same prices as competition.
4. Auction type pricing
The most popular modern example of auction type pricing is eBay who provides a platform for its customers to both buy and sell. Usually, there are three types of auctions (interestingly enough, country-related in name):
- English auctions – there is only one seller with many buyers who bid on the item until the best price is reached;
- Dutch auctions – either one seller and many buyers or one buyer and many sellers, with the process backwards to English auctions in the first case as the top price is first announced and then slowly lowering in bidding or the buyer announcing the product he wishes to buy and then the sellers bidding their best offers to him;
- Sealed-bid auctions – common for large orders or contracts, particularly in the industrial and government departments, where companies submit their bids in sealed envelopes in response to a tender, not disclosing the bid to anyone.
5. Differential pricing
Differential pricing is used in cases where companies charge different prices to a different group of customers for the same product or service. This pricing method depends on factors such as place, time and product form, thus varying in offering. An example would be a 0.33 can of Coca-Cola which has different prices in grocery stores, public stations, and especially hotel rooms with their super-pricy minibars.

An example of differential pricing based on a 0.33 can of Coca-Cola (Image source: SlideShare)
Conclusion
Pricing methods present a way to determine a price of your offering by accounting factors various like the costs, the product itself, competition, target audience, their perceived value, product’s life cycle and so on, having a great deal of impact on the pricing strategy as a whole. When it comes to pricing methods, a business has its pick of the litter. As evidenced, there is a variety of options for selecting a pricing method that best suits the needs of a thriving business. Hence, it can adopt any of mentioned pricing methods depending on the type of a product it sells and the end goal objective for which a business is determining the pricing.
If you found this useful and you’d like to learn how to take your pricing strategy to the next level, we invite you to download our free 20 secrets to designing the best pricing strategy eBook. Click below to take advantage of this opportunity.